
Exhibition time: 17-19 March, 2026 Shanghai, China
 中文
中文

Exhibition time: 17-19 March, 2026 Shanghai, China
 中文
中文
Highlights
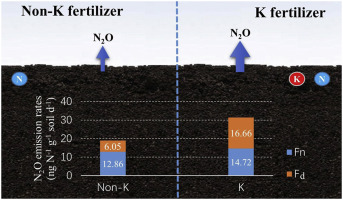
•K fertilizer application significantly increased N2O emissions in agricultural acid soil.
•Denitrification was an important pathway of N2O production in agricultural acid soil.
•Potassium fertilizer increased the contribution of denitrification to N2O emission.
Abstract
Potassium (K) fertilizer plays an important role in increasing crop yield, quality, and nitrogen use efficiency. However, little is known about its environmental impacts, such as its effects on emissions of the greenhouse gas nitrous oxide (N2O). A nitrogen-15 (15N) tracer laboratory experiment was therefore performed in an acidic agricultural soil in the suburbs of Wuhan, central China, to determine the effects of K fertilizer on N2O emissions and nitrification/denitrification product ratios under N fertilization. During 15-d incubation periods with a fixed initial N concentration (80 mg kg−1), K application increased average N2O emission rates significantly (1.6–10.8-fold) compared to the control treatment. N2O emissions derived from nitrification and denitrification both increased in K-treated soil, and denitrification contributed more to the increase; its contribution ratio rose from 32% without K fertilizer to 53% with 300 mg kg−1 of K applied. The increase in N2O emissions under K fertilization is probably due to an increase in the activity of denitrifying microorganisms and acid-resistant nitrifying microorganisms caused by higher K+ concentrations and lower soil pH. Combined treatment with potassium chloride (KCl) and N fertilizer produced lower N2O emissions than combined treatment with potassium sulfate (K2SO4) and N fertilizer during 15-d incubation periods. Our results imply that there are significant interaction effects between N fertilizers and K fertilizers on N2O emissions. In particular, combining N fertilizers with fertilizers that reduce soil acidity or contain Cl or K ions may significantly affect agricultural N2O emissions.
Graphical abstract
From ScienceDirect
