
Exhibition time: 17-19 March, 2026 Shanghai, China
 中文
中文

Exhibition time: 17-19 March, 2026 Shanghai, China
 中文
中文
The carbon dioxide fertilization or carbon fertilisation is not only the cause of plant growth but also contributes the greening effect. It is the phenomena that the increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases the rate of photosynthesis in plants. In this article, we are given the definition of Carbon Fertilization and its effect on crop production which is very useful for the competitive examinations like UPSC-prelims, SSC, State Services, NDA, CDS, and Railways etc.
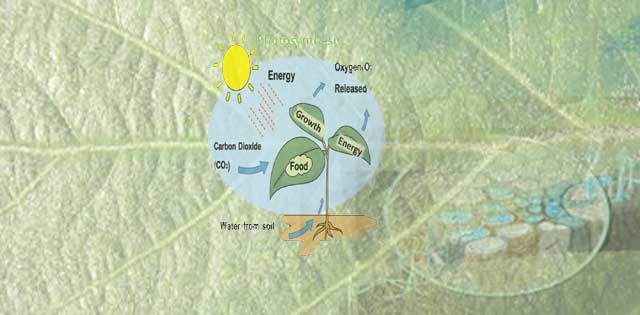
Carbon Fertilization and its effect on crop production, Carbon Fertilization, how does carbon fertil
The entire world, making their efforts to restrain, halt and/or reverse the climate change through management strategies, behavioural changes and technological innovations that reduce the emission of Greenhouse Gases (GHGs). According to the some environmentalists that Carbon Fertilisation can be new weapon in the carbon fight.
Carbon fertilization is also known as Carbon Dioxide Fertilisation. It is the phenomena that the increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases the rate of photosynthesis in plants.
1. Carbon Dioxide fertilisation on plants
2. Global Warming
3. Depletion of ozone layer in the stratosphere
How Organic Farming helps in Carbon Sequestration?
Soils are a major carbon reservoir containing more carbon than the atmosphere and terrestrial vegetation. The anthropogenic impacts on soil can turn it into either a net sink or a net source of Greenhouse Gases (GHGs). After carbon enters the soil in the form of organic material from soil fauna and flora, it can persist in the soil for decades, centuries or even millennia. Eventually, soil organic carbon can be lost as CO2 or CH4 emitted back into the atmosphere, eroded soil material, or dissolved organic carbon washed into rivers and oceans.
The dynamics of these processes highlight the importance of quantifying global carbon fluxes to ensure maximum benefits of soil organic carbon to food production, and water and climate regulation. The effect varies depending on the plant species, the temperature, and the availability of water and nutrients. The effect of carbon fertilization on crop production is given below:
1. The green leaves of the plant use energy from sunlight through photosynthesis to chemically combine carbon dioxide drawn in from the air with water and nutrients tapped from the ground to produce sugars, which are the main source of food, fiber and fuel for life on Earth.
2. Increase of anthropogenic emission: The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere helps in the growth of plants because the rate of photosynthesis increases will resulted the rise of anthropogenic emissions. Plants grow faster leads to the sequestration of more Carbon dioxide and the growth also increases the crop yields. In other words, larger amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere that has resulted from rising anthropogenic emissions will help in the growth of plants, which use carbon dioxide during photosynthesis.
3. Increases the efficiency of water utility in the plants: During high concentration of carbon dioxide, plants maintain narrow openings of leaf surface which protect them in water loss.
4. Plants distribute a greater proportion of photosynthate to roots under high concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide. This resulted greater root production, which increases the development of mycorrhiza and fixation of nitrogen in root nodules. It helps the plants to grow even less nutritional soil.
5. The reproductive biomass growth as well as vegetative biomass growth is usually increased by elevated carbon dioxide.
In the above discussion, it shows that the increased concentrations of carbon dioxide increase the photosynthesis which ultimately helps in the growth of plants. Hence, we can say that carbon dioxide fertilization or carbon fertilisation is not only the cause of plant growth but also contributes the greening effect.
From Jagranjosh
