
Exhibition time: 17-19 March, 2026 Shanghai, China
 中文
中文

Exhibition time: 17-19 March, 2026 Shanghai, China
 中文
中文

Key words of the passage: microalgae; metabolites; biological; fertilizer
Recently, Beijing Protoga Biotech and Crop Nutrition Team of Syngenta published scientific research results entitled Extracellular Metabolites of Heterotrophic Auxenochlorella protothecoides: A New Source of Bio-Stimulants for Higher Plants in the journal Marine Drugs , expanding the application of microalgae To the agricultural field, to explore the potential of microalgae tailings as bio-stimulant. PROTOGA BIOTECH and Syngenta team has discovered and verified the feasibility of extracellular metabolites in the tail water of microalgae as a new type of biological fertilizer, enhancing the economic value and environmental friendliness of the whole process of industrial production of microalgae.
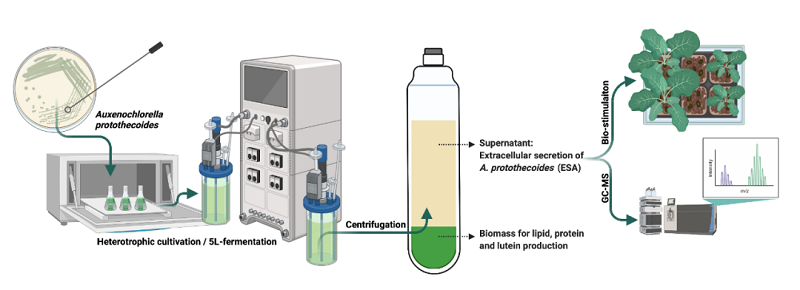
▲Figure 1. Graphical abstract (source: research paper)
The production of modern agricultural crops depends to a large extent on chemical fertilizers, but the excessive use of chemical fertilizers can easily cause environmental pollution of soil, water and air and food safety problems. Green agriculture is a sustainable agricultural development model proposed by China in recent years. With "green environment", "green technology" and "green products" as the main aim, it promotes the transformation of chemical agriculture that relies too much on chemical fertilizers and pesticides to ecological agriculture that mainly relies on the internal mechanism of biology .
Microalgae are tiny photosynthetic organisms found in freshwater and marine systems that produce many different biologically active substances, such as proteins, lipids, carotenoids, vitamins and polysaccharides. Studies have reported that microalgae such as Chlorella vulgaris, Scenedesmus, Cyanobacteria, and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii can be used as bio-modifiers for agricultural products such as sugar beet, tomato, and alfalfa, helping to improve the seed germination rate, active substance accumulation and growth and development of crops.
Auxenochlorella protothecoides is a single-celled eukaryotic microalgae that can grow both autotrophically using light and carbon dioxide, and growing heterotrophically using glucose. It is one of the important microalgae producing oils and proteins. Chlorella protothecoides can accumulate a large amount of fatty acids, proteins and lutein, and the cell density of heterotrophic culture can reach about 100-1000 times that of autotrophic culture. The waste water (tail water) after the fermentation of Chlorella protothecoides is generally discharged after water treatment, which increases the production cost.
In order to turn waste into treasure, realize the reuse of tail water and increase economic value. Protoga Biotech and Syngenta's China Crop Nutrition Team have cooperated to study the effect of Chlorella protothecoides tailing water (EAp) on the growth of higher plants, and can also improve its resistance to stresses.
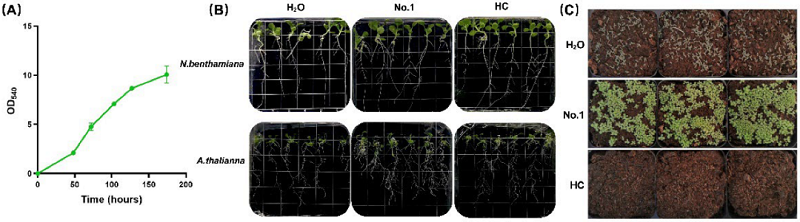
▲ Figure 2. The effect of EAp on the growth of model plants (source: research paper)
The team worked together to identify and analyze extracellular metabolites in the tail water, and found that there are more than 84 compounds in EAp, including 50 organic acids, 21 phenolic compounds, and active substances such as oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
It provides a basis for EAp to develop new biological fertilizers and its comprehensive utilization in agriculture, and analyze its possible mechanism of action: 1) The release of organic acids can promote the dissolution of metal oxides in the soil, thereby increasing iron, zinc and copper 2) Phenolic compounds have antibacterial or antioxidant effects, strengthen cell walls, prevent water loss, or function as signaling molecules in developmental processes such as cell division, hormone regulation, photosynthetic activity, nutrient mineralization, and reproduction 3) Microalgal polysaccharides can increase the content of ascorbic acid in plants, increase the activities of NADPH synthase and ascorbate peroxidase, thereby affecting the photosynthesis, cell division and abiotic stress tolerance of plants.
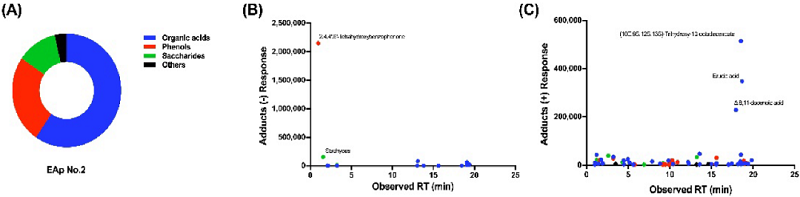
▲Figure 3. Metabolite analysis of EAp No.2 (source: research paper)
During the industrial production of microalgae, the extracellular metabolites (EAp) of Chlorella protothecoides are usually treated as waste tails. This study found that EAp can promote plant growth, enrich nutritional value and improve abiotic stress resistance. . Among them, EAp No.2 and No.3 can also promote plant growth under high dilution factor, and provide transportation convenience for their practical application. The commercial application of EAp not only makes the industrial chain of the microalgae industry more complete and maximizes value benefits, but also provides new environmental protection solutions for agricultural development, while achieving green and sustainable production and application. The composition research and mechanism analysis of EAp provide a theoretical basis for the application of microalgae tailings, and open the door for Protoga Biotech to develop new, more economical and greener microalgae agricultural bio-improvers with the Syngenta China Crop Nutrition Team.
References:1. Qu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ma, B.; Zhu, H.; Zheng, X.; Yu, J.; Wu, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, Y . Extracellular Metabolites of Heterotrophic Auxenochlorella protothecoides: A New Source of Bio-Stimulants for Higher Plants. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20090569
