
Exhibition time: 17-19 March, 2026 Shanghai, China
 中文
中文

Exhibition time: 17-19 March, 2026 Shanghai, China
 中文
中文

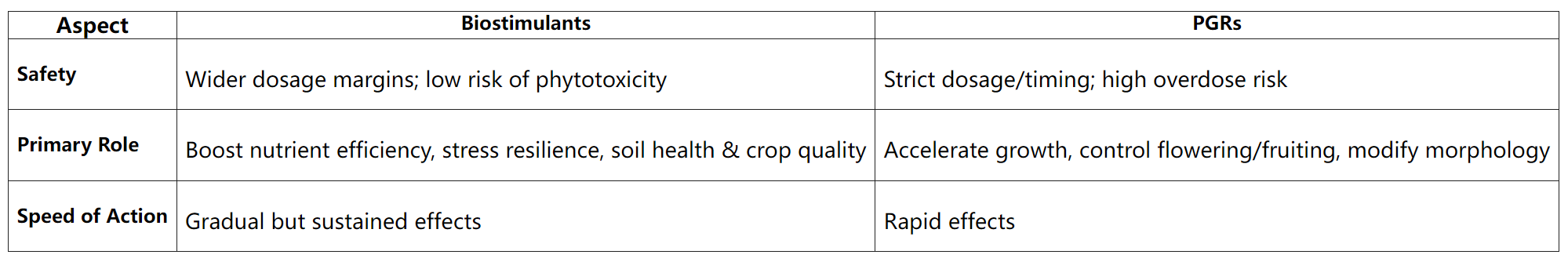
Biostimulants:
Naturally derived substances (e.g., seaweed extracts, humic acids, amino acids, chitosan) obtained via bioprocessing, not chemical synthesis. Defined by the EU as "products stimulating plant nutrition processes independently of the nutrient content".
Plant Growth Regulators (PGRs):
Synthetic chemicals or microbial extracts that mimic endogenous plant hormones (e.g., auxins, gibberellins) to directly alter growth patterns.
Biostimulants:
Indirect: Enhance nutrient uptake, stress tolerance (drought/salinity), and soil health by activating plant metabolic pathways or soil microbiology.
Do not alter plant hormones.
PGRs:
Direct: Interfere with hormonal signaling (e.g., cell division, flowering, fruit set) by overriding natural plant physiology.
EU: Classifies biostimulants under fertilizer regulations (excluded from pesticides).
USA: Some biostimulants regulated as pesticides due to bioactive claims.
China: PGRs require pesticide registration; biostimulants lack unified regulation.
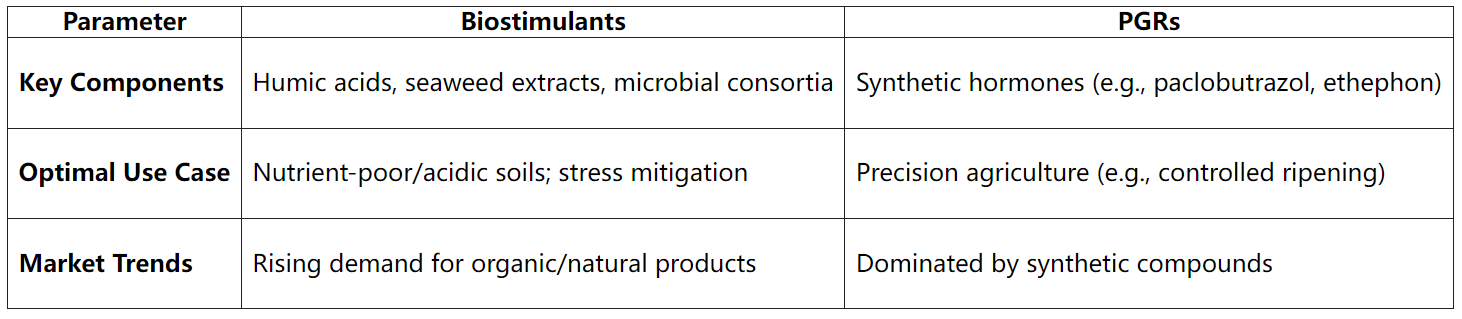
Core Difference:
Biostimulants enhance natural plant processes (non-hormonal), improving resilience and efficiency. PGRs directly override plant physiology via hormonal manipulation for targeted outcomes. Combined use can optimize yield while reducing ecological impact.
[1]: Du Jardin, P. (2015). Plant Science
[2]: EU Fertilizing Products Regulation (2019/1009)
[3]: Rouphael & Colla (2020). Frontiers in Plant Science
[4]: China Pesticide Registration Guidelines
[5]: Yakhin et al. (2017). Plant and Soil
[6]: Global Biostimulants Market Report (2023)