
Exhibition time: 17-19 March, 2026 Shanghai, China
 中文
中文

Exhibition time: 17-19 March, 2026 Shanghai, China
 中文
中文
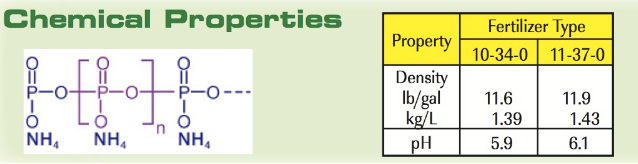
Key words of the passage: polyphosphate; agricultural; fertilizer; production; use
In polyphosphate fertilizer, between half and three-quarters of the phosphorus is temporarily locked up by chained polymers. The remaining phosphorus (orthophosphate) is immediately available for plant uptake. With exposure to the soil, enzymes produced by soil microorganisms and plant roots break down the polymer phosphate chains into simple phosphate molecules the plants can digest, though some of the polyphosphates will decompose even without the enzymes. The enzyme activity goes faster in moist, warm soils. Typically, half of the polyphosphate compounds are converted to orthophosphate within a week or two for plant uptake. Under cool and dry conditions, the conversion may take longer.
Since polyphosphate fertilizers deliver nutrients both immediately and gradually via their combination of both orthophosphates and polyphosphates, plants can use them very effectively, longer.
Fluid fertilizers are commonly used in production agriculture, but not widely applied by homeowners. Farmers like them for their convenience and balanced nutrient distribution, since liquid fertilizers easily blend with many other nutrients and chemicals, and each drop of fluid is identical to the next. For most situations, growers choose between dry and liquid based on the price of nutrients, fertilizer-handling preferences and preferred field practices rather than significant agronomic differences.
Source: https://www.cropnutrition.com/resource-library/polyphosphate

Previous: Township turns waste straw into profit